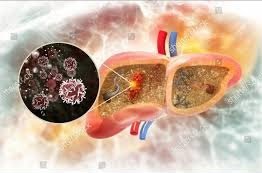
Liver cancer, also known as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), is a serious and potentially life-threatening disease that affects thousands of individuals each year. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of liver cancer, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Causes of Liver Cancer
Liver cancer typically develops as a result of prolonged damage to the liver. The primary risk factors for liver cancer include chronic viral hepatitis infections, particularly hepatitis B and C, as well as excessive alcohol consumption, obesity, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Cirrhosis, a condition where healthy liver tissue is replaced with scar tissue, is another significant precursor to liver cancer.
Symptoms of Liver Cancer
Liver cancer often remains asymptomatic in its early stages, making it difficult to detect. However, as the disease progresses, patients may experience the following symptoms:
1. Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes due to impaired liver function.
2. Abdominal Pain: Discomfort or pain in the upper right side of the abdomen.
3. Unexplained Weight Loss: A sudden and unexplained drop in weight.
4. Loss of Appetite: A decreased desire to eat, leading to weight loss.
5. Fatigue: Feeling constantly tired and weak.
6. Swelling: Swelling or fluid buildup in the abdomen or legs.
Diagnosis of Liver Cancer
Diagnosing liver cancer usually involves a combination of medical history evaluation, physical examination, and various diagnostic tests. Common diagnostic methods include:
1. Blood Tests: Blood tests can reveal elevated levels of certain liver enzymes and tumor markers, which may indicate the presence of liver cancer.
2. Imaging Scans: CT scans, MRI scans, and ultrasound can provide detailed images of the liver and help identify tumors.
3. Liver Biopsy: A sample of liver tissue is collected and examined under a microscope to confirm the presence of cancer cells.
4. Angiography: This procedure uses a contrast dye and X-rays to visualize blood vessels in the liver and detect tumors.
Treatment Options
The choice of treatment for liver cancer depends on various factors, including the stage of cancer, the patient’s overall health, and the extent of liver damage. Treatment options include:
1. Surgery: Surgical removal of the tumor or a liver transplant may be considered if the cancer is detected early and hasn’t spread extensively.
2. Ablation Therapy: Techniques such as radiofrequency ablation and microwave ablation use heat to destroy cancerous tissue.
3. Radiation Therapy: High-energy X-rays are used to target and kill cancer cells.
4. Chemotherapy: Medications are administered to kill cancer cells or slow their growth.
5. Targeted Therapy: Drugs are used to target specific molecules involved in cancer growth.
6. Immunotherapy: This treatment boosts the body’s immune system to fight cancer cells.
Prevention and Conclusion
Preventing liver cancer involves reducing risk factors such as hepatitis infections, alcohol abuse, and obesity. Vaccination against hepatitis B, regular liver screenings for at-risk individuals, and adopting a healthy lifestyle can contribute to prevention.
In conclusion, liver cancer is a formidable disease that demands early detection and timely intervention. Understanding its causes, recognizing its symptoms, and seeking prompt medical attention can significantly improve the chances of successful treatment. As ongoing research continues to uncover new therapies and prevention strategies, there is hope for better outcomes for individuals at risk of liver cancer.